How to make a folder common to all computers on the network. Setting up shared access to a folder over a network in Windows The shared folder does not work
In the Windows operating system, you can connect shared access to a folder on a local home network to exchange data between computers using shared folders. This is a very convenient and fast way to transfer files computer-to-computer, without using external media (flash drives, external hard drives, memory cards, etc.).
In this article I will talk about creating a local network using the Windows 10 operating system as an example. Creating and setting up a local network in Windows 8 and Windows 7 is done in a similar way; these instructions are universal.
The article discusses the following option for using shared folders on a local network: several computers are connected to the router, connected via cable and wireless Wi-Fi network, united into a home network. A shared folder is created on each computer; all computers included in this local network have access to the shared folders.
On computers connected to the home local network, the operating systems Windows 10, Windows 8, Windows 7 (different OS, or the same operating system) can be installed, connected to the router via Wi-Fi or cable.
Creating and configuring a local network takes place in four stages:
- the first stage is checking the workgroup name and network card settings
- second stage - creating and configuring local network parameters
- third stage - connecting shared access to a folder on the local network
- fourth stage - data exchange over the local network
First you need to check the workgroup settings and network card settings, and then create a local Windows network.
Checking network card and workgroup settings
On the Desktop, right-click on the “This PC” icon (“My Computer”, “Computer”), select “Properties” from the context menu. In the “System” window, click on “Advanced system settings”.
In the “System Properties” window that opens, open the “Computer name” tab. Here you will see the workgroup name. By default, in Windows 10, a workgroup is named "WORKGROUP".

On all computers connected to this local network, the workgroup name must be the same. If the workgroups have different names on the computers you connect to the network, change the names by choosing one name for the workgroup.
To do this, click on the “Change...” button, in the “Changing computer or domain name” window, give a different name for the workgroup (write the new name in capital letters, preferably in English).
Now check your network card settings. To do this, in the notification area, right-click on the network icon (Internet access). Click on "Network and Sharing Center". In the Network and Sharing Center window, click the Change adapter settings link.
In the Network Connections window, select a network card, Ethernet or Wi-Fi, depending on how your computer connects to the Internet. Next, right-click on the network card and click on “Properties” in the context menu.
In the network card properties window, in the “Network” tab, select the “IP version 4 (TCP/IPv4)” component, and then click on the “Properties” button.

In the Internet Protocol Properties window that opens, in the “General” tab, check the IP address and DNS service settings. In most cases, these parameters are assigned automatically. If these parameters are inserted manually, check the corresponding addresses with your Internet provider (the IP address on computers connected to the network must be different).

After checking the settings, you can proceed directly to creating a local network in Windows.
Creating a local network
First of all, configure the local network settings in Windows. Enter the “Network and Sharing Center”, click on the “Change advanced sharing settings” item.
The Advanced Sharing Settings window allows you to change sharing settings for different network profiles. The Windows operating system creates a separate network profile with its own special parameters for each network used.
There are three network profiles available:
- Private
- Guest or public
- All networks
In your private network profile, under Network Discovery, select Enable Network Discovery.
In the File and Printer Sharing option, enable the Enable File and Printer Sharing option.
In the HomeGroup Connection option, select Let Windows manage HomeGroup connections (recommended).

After that, open the “All Networks” network profile. In the Public Folder Sharing option, select Enable sharing to allow network users to read and write files in public folders.
In the File Sharing Connection option, select the Use 128-bit encryption to secure sharing connections (recommended) option.
In the “Password Protected Sharing” option, enable the “Turn off Password Protected Sharing” option.

After completing the settings, click on the “Save Changes” button.
Repeat all these steps on all computers that you plan to connect to your home local network:
- check the workgroup name (name must be the same)
- check your network card settings
- In sharing settings, enable network discovery, enable file and printer sharing, disable password protected sharing
How to enable folder sharing
In this case, I created a folder named “General”. Right-click on this folder and in the folder properties window, open the “Access” tab.
Then click on the “Advanced setup” button.

In the “Advanced sharing settings” window, activate the “Share this folder” option, and then click on the “Permissions” button.

Select permissions to use shared folder data from another computer. There are three options to choose from:
- Full access
- Change
- Reading

To save the settings, click on the “OK” button.
Go back to the folder properties, open the “Security” tab, and then click on the “Change...” button.

In the window that opens, enter the name “Everyone” (without quotes) in the “Enter names of selected objects” field, and then click on the “OK” button.

In the folder properties window, in the “Security” tab, configure the permissions that you previously selected for the shared folder.

To change the permission for the “Everyone” group, click on the “Advanced” button. In the “Advanced security settings for a shared folder” window, select the “Everyone” group, and then click on the “Change” button to change permissions.
Setting up a local network in Windows is complete. In some cases, you may need to restart your computer for all changes to take effect.
Logging into your local home network
Open Explorer, in the “Network” section you will see all available computers connected to your local home network. To log into another computer, click on the computer name, and then click on the shared folder name to access the files and folders located in the shared folder.

The local network in Windows 10 has been created and configured.
Troubleshoot some network problems
Sometimes, after setting up the network, problems arise with accessing folders on the local network. One possible problem may be an incorrectly selected network profile. I encountered this myself on my computer. After reinstalling the system, I created and configured a local network, but my computer did not see two laptops connected to this network. From the laptop I could easily access the shared folder on my computer, but the computer did not see them at all.
I checked all the local network settings several times, and only then I noticed that my computer was running a public network, and not a private (home) network, like on laptops. How can such a problem be solved?
Enter the “Network and Sharing Center”, click on “Troubleshooting”. Select the “Shared Folders” section and run diagnostics and troubleshooting. At the very end, the application will offer to configure the network as private. Apply this fix, and then restart your computer. After performing this operation, my computer gained access to shared folders on laptops on the local network.
Often problems arise due to incorrect network configuration. Windows 10 has the option to reset network settings to default settings. Go to “Settings”, “Network and Internet”, in the “Change network settings” section, click on “Reset network” to apply the default network settings.
Other problems may arise; look for solutions on the Internet.
Conclusion
In Windows OS, you can create a local private (home) network between computers, organize data exchange using shared folders, and gain access to a printer. Computers on the same network can have different or the same operating systems installed (Windows 10, Windows 8, Windows 7).
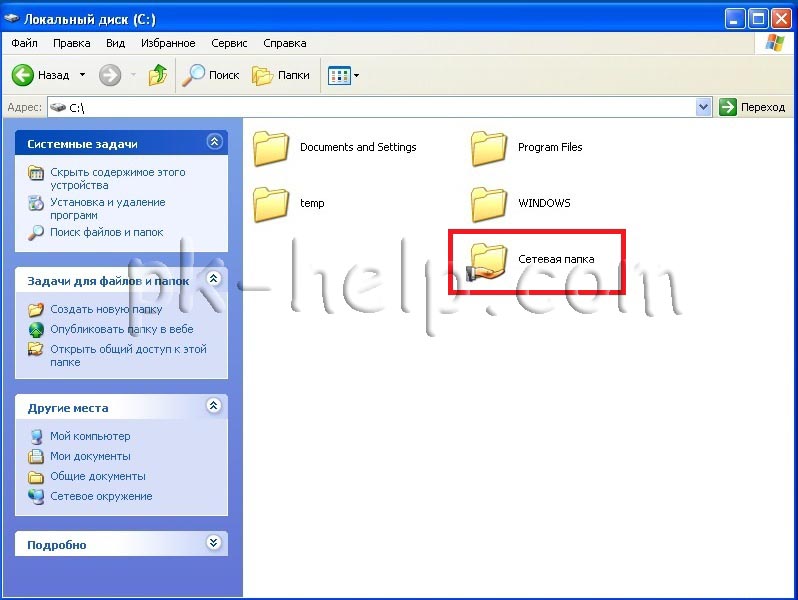
In order to make a network folder in Windows XP, create a folder, for example "Network Folder", right-click on it and select " Properties".
In the properties window, go to the " tab Access" and check the boxes next to " Share this folder", if it is necessary that network users can change (add, delete) files in this folder, check the box - " Allow modification of files over the network".

At this point, the creation of a network folder (called a “share”) can be considered complete. As you can see, a hand has appeared at the bottom of the folder, this means that the folder is network.
In order for other users to see it on the network, you need to go to network , choose " Show workgroup computers", find the computer on which the network (shared) folder is located, click on it and see the network shared folder there.

You can click "Start" - "Run" or keyboard shortcut "Win" + "R", enter //<имя или IP компьютера> , For example //comp, press the Enter key, all shared folders on the computer will open.

network drive .
How to make a network folder in Windows 7.
Properties".

In the properties window, go to the "tab" Access" and press " General access".

Now you need to add the necessary users and give them the appropriate access; in this example, everyone will have full access (the ability to change and delete files) to the folder. In the Add field select " All", in column Permission level select " Read and Write", press " General access".

Ready".

After that, go to " Start" - "Control Panel" -" or click on the button Network connection on the taskbar and select "Network and Sharing Center".

In the window that opens Network and Sharing Center look at what network is being used (in this example - Work) click on "".
 In the profile you are using (home, work or general), make the necessary changes, namely:
In the profile you are using (home, work or general), make the necessary changes, namely:

Scroll down and:
Save your changes.

At this point, setting up a network folder in Windows 7 can be considered complete.
Computer, on the right click " Net", select the computer on which the network folder is located, all shared folders on the computer will open on the right.

Another way is to click "Start" or keyboard shortcut "Win" + "R" and enter //<имя или IP компьютера> , For example //User-PC.

For ease of use, you can connect a network folder network drive .
How to make a network folder in Windows 8.
In order to make a network folder in Windows 7, create a folder, right-click on it and select " Properties".

In the properties window, go to the "tab" Access" and press " General access".

Now you need to add the necessary users and give them the appropriate access; in this example, everyone will have full access to the folder (the right to change and delete files). In the Add field select " All" and in the column Permission level select " Read and Write", press " General access".

A message window will open indicating that the pack has become online. Click " Ready".

After that, go to "Control Panel" - "Network and Sharing Center""or click on the Network Connection button on the Taskbar and select "Network and Sharing Center".

In the window that opens, look at what network is being used (in this example - Public) click on " Change advanced sharing options".
 In the profile you are using (private, guest or public), make the necessary changes, namely:
In the profile you are using (private, guest or public), make the necessary changes, namely:
Enable network discovery;
Turn on file and printer sharing;

Go to the "tab" All networks":
Enable sharing to allow network users to read and write files in shared folders.

Disable password protected sharing.

Save your changes.
At this point, setting up a network folder in Windows 8 can be considered complete.
To use the network folder, go to Computer, on the right click " Net", select the computer on which the network folder is located, by clicking on the required computer, all its shared folders will open on the right.

Another way is to press the keyboard shortcut "Win" + "R", enter //<имя или IP адрес компьютера> , For example //pk2. By pressing Enter, a window with shared computer folders will open.

For convenience, the shared folder can be connected network drive .
I hope now you, regardless of the operating system Windows XP/Windows 7/Windows 8, can share the folder without any problems.
Hello! For those who are not in the know, I’ll start from afar. On computers and laptops with Windows installed, there is a separate “Network” tab in Explorer. This tab displays devices from the network environment. That is, by opening the “Network” tab, we can see there computers, network storage (NAS), multimedia devices (DLNA), flash drives and external drives that are connected to the router and to which shared access is configured. Simply put, those devices that are connected through one router (located on the same network) and on which network discovery is enabled (devices that can be discovered on the local network). Our router may also be displayed there (section "Network infrastructure") and other devices.
Now I’ll explain what and how, and why I decided to write this article. I have an ASUS router, to which I connected a USB flash drive, and configured shared access to this flash drive for all devices on the network. And what do you think, this network drive appeared in the “Network” section on all computers (it is displayed there as "Computer"), but it didn’t show up on my computer. That is, my computer did not see the flash drive connected to the router, nor other computers on this network. But the DLNA server was displayed running on the same router. But this does not change anything, since I need regular network access to the drive.
Also, I could not access the flash drive when I typed its address //192.168.1.1 in Explorer. This address was immediately opened through the browser. And I was unable to connect this drive as a network drive. It simply was not in the list of available devices in the network environment.
Such a problem when Windows 7, Windows 8, or Windows 10 does not see network devices is not uncommon. It doesn't have to be a flash drive or an external HDD that you connected to your router, as in my case. Most often, shared access is configured between computers on a local network. And they face the same problem when computers are connected to the same network (to one router), the sharing settings are set correctly, but the "Network" tab is empty. Or only the router and your computer are displayed.
Since there can be many reasons and, accordingly, solutions, I’ll probably start with the simplest ones (which didn't help me) and at the end of this article I will share the solution that helped in my case. As a result, my laptop still saw all the devices on the network. Including a network storage device and another computer that is also connected to this network.

But this does not mean that you have the same case. Therefore, I advise you to check all the settings in order.
Checking sharing settings
We will consider two cases:
- When computers do not see each other on the local network.
- Sharing access to a network storage device. This can be a flash drive, or a hard drive that is connected to the router, or a separate drive (aka NAS).
First case
For computers to be able to see each other and appear in the Network section in Explorer, they must be connected through the same router. Or connected directly (cable or via Wi-Fi). Simply put, they must be on the same local network.
Next, on all computers (I don’t know how many of them you have there), it is advisable to assign the network status to “Home” (private). I wrote in the article how to do this in Windows 10. In Windows 7, just go to the Network and Sharing Center and change the status of the current connection there.

If after this the computer still does not detect other computers (or vice versa), then let's also check the sharing settings.
To do this, in the “Network and Sharing Center” window (if you don’t know how to open it in Windows 10, then see the article), click on the “Change advanced sharing settings” item.

And for the current profile we set the parameters as in the screenshot below.

Let's do it on all computers on the local network.
Articles on this topic:
As a rule, these tips solve all problems with detecting computers on a local network.
Second case
When you have problems accessing your network storage. As in my case. Windows 10 did not see the USB drive that was connected to the ASUS router. Now many routers have a USB port for connecting drives and other devices, so the topic is relevant.
You need to make sure that this drive is defined in the router settings and that sharing is enabled. It is clear that this is done differently on different routers. On ASUS routers, for example, it looks like this:

Related articles:
Do not confuse sharing settings with FTP settings. The FTP server settings on the router have nothing to do with this.
Well, if other devices see the network storage and have access to it, but on a particular computer there is no access to it, then the problem is not on the router’s side. Go through the settings of the “problem” PC using this article.
An antivirus or firewall may be blocking network devices
If your antivirus or firewall (firewall) that is installed on your computer doesn’t like something, then it can easily make it so that neither you can see other devices in the network environment, nor can anyone detect you.
True, after disabling the firewall built into my antivirus, the problem was not solved (which means the problem is most likely not there), but it still seems to me that in my case it could not have happened without the participation of the antivirus.
Therefore, try to completely stop the antivirus for a while, or at least disable the firewall built into it (firewall). In NOD 32 this is done like this:

To check this you need to do on all computers, which will participate in the local network.
It is quite possible that you have some other programs installed that can monitor the network and manage network connections.
If it turns out that the problem is in the antivirus, then you need to add your network to the exceptions. Prevent the firewall from blocking the network itself or network devices.
If you don’t have an antivirus, you can experiment with disabling/enabling the firewall built into Windows.
Working group
The workgroup must be the same on all devices. As a rule, this is true. But it is advisable to check. To do this, open the computer properties "System" and go to "Advanced system settings".
"Working Group" will be indicated there. To change it, you need to click on the "Change" button.

Once again: the workgroup name must be the same on all computers.
If you have a problem accessing your network storage (to flash drive via router), then in the sharing settings on the same ASUS router the work group is also indicated. You can look at the screenshot above in the article. It should be the same as on the computer.
Problem accessing a shared network folder via SMB1 in Windows 10 (my solution)
Let's return specifically to my problem. Everything I described above has been checked and rechecked 10 times already. I did it a couple of times, but Windows 10 never saw other computers on the network and, most importantly, the shared folder in the form of a flash drive connected to the router never appeared in Explorer. And on other devices on the network everything was detected without problems. Including my laptop.
I read somewhere that you can try opening a shared folder through the Run window. Pressed the Win + R key combination and entered the network folder address //192.168.1.1 (aka router address).
I did not gain access to the drive, but an interesting error appeared:
You cannot connect to the shared folder because it is not secure. This shared folder runs on the legacy SMB1 protocol, which is insecure and may expose your system to attack.
Your system needs to use SMB2 or later.

This is already interesting. At least something.
SMB (Server Message Block) is a network protocol that is responsible for sharing access to files, printers and other network devices.
I started looking. And it turns out that Windows 10 abandoned the SMB1 protocol. Because of safety. And the Samba software package installed on my router seems to work using the SMB1 protocol. That's why Windows 10 doesn't see it. But other computers that also run Windows 10 were also not displayed on the “Network” tab.
Since I couldn’t update the protocol for SMB2 in the router settings, I decided that I needed to somehow enable SMB1 support in Windows 10. And as it turned out, this can be done without any problems. As a result, after connecting the “SMB Client 1.0/CIFS” component, everything worked for me. The system saw shared folders on computers on the network and a network folder configured on the router itself.
How to enable SMB1 in Windows 10?
Through the search, find and open the old “Control Panel”.

Switch to Small Icons and open Programs and Features.

Open "Turn Windows features on or off". Find the item “Support for SMB 1.0/CIFS file sharing”. Open it and check the box next to "SMB Client 1.0/CIFS". Click Ok.

If your computer prompts you to restart, restart it. If there is no prompt window, reboot manually.
After the reboot, all available devices on your network should appear on the “Network” – “Computer” tab.
I will be glad if this article is useful to someone and helps solve the problem that has arisen. Don't forget to write in the comments about the results. Or ask the question, where would we be without them :)
The latter, despite a lot of advantages, is still inferior in many respects. For example, unlike the paid VMware Workstation, VirtualBox is completely free. And if the virtual machine is created in 64-bit Windows, you can install a 32-bit Windows guest on it using VirtualBox. A 32-bit guest OS will work a little faster than a 64-bit one, which, due to the conditions of the VMware Workstation program, will need to be installed on a virtual machine that is also based on 64-bit Windows.
But where VirtualBox unconditionally loses is in the process of setting up a shared folder for the main and guest OS. In the VMware Workstation program, this process, which, by the way, was discussed earlier on the site, is simplified to the extreme. While in the VirtualBox program, setting up a shared folder will require several separate steps - assigning a shared folder, installing special guest OS additions and connecting the shared folder to display in Explorer using the Windows command line.
Well, the road will be mastered by those who walk, so let’s get down to business directly.
But first, about the mandatory conditions. To add a shared folder, the virtual machines in VirtualBox for which these folders are mounted must be shut down, not suspended and saved.
1. Adding a shared folder for the main and guest OS
We select the virtual machine for which you need to configure a shared folder with the main OS, if several of these (virtual machines) have been created. In the VirtualBox manager window, click the button on the program toolbar “ Tune».
The virtual machine settings window will open. On the left select the section “ Shared folders" On the right, click the button in the form of a folder with a plus sign - this is a browse button for selecting a folder that is intended to be shared with the main and guest OS. In Explorer, select a folder on a real computer or create a new one specifically for working with two systems. In the window for adding a shared folder, check the option “ Auto-connection" and click " OK" To protect yourself from the possible penetration of malware from the guest OS into the main OS, you can set the option “ Only for reading" In this case, files placed in a shared folder in the main OS can be opened or copied to any other location in the guest OS. But it will not be possible to fill the shared folder with guest OS files.

2. Installing guest OS additions
Now we launch the virtual machine, for which a shared folder with the main OS is configured. In the VirtualBox window menu at the top, select the section “ Devices", and in it - the command " Mount the Guest OS Additions disk image».


In the VirtualBox add-ons window that opens, select the launch file.

Then we follow the step-by-step wizard for installing VirtualBox add-ons. In the first window, click “ Next».

In the second window, also click “ Next».

In the third click " Install».

The last window for installing VirtualBox add-ons will notify you that you need to reboot the virtual machine. We agree and click “ Finish».

3. Mounting a shared folder using Windows command prompt
When the virtual machine reboots, in rare cases the shared folder may immediately appear in Windows Explorer under " Net" But, alas, what often happens in practice is that the folder is not displayed in Explorer. And for this to happen, you need to do some things using the command line. Call the command line. If Windows 7 is installed as a guest OS, you can open the Command Prompt from the Start menu. If it is not in quick access, look for it in the menu search. Call the command line as administrator.

If installed as a guest OS, the command line with administrator rights is available in the list of context menus called up on the " Start».

In the command line window, enter a command like:
net use drive_letter: \\vboxsvr\folder_name
In our case, drive X is selected, and the shared folder is named “Shared_folder”. Therefore the command will look like this:
net use x: \\vboxsvr\Shared_folder
Enter the command and press Enter.

Now open Windows Explorer. And in the “This computer” section with the “Network locations” subsection expanded, we will see a shortcut to the shared folder of the main and guest OS. Let's click on it.

If the shared folder shortcut in “Network Locations” is not displayed, reboot the virtual machine. To ensure easy access to the shared folder in the guest OS, we can place a shortcut to it on the desktop.

That’s it – the shared folder for the main and guest OS has been created. We can test it. Let's place a file in a shared folder on a real computer and open it from a shared folder on a virtual machine.

Did this article help you?